Decision support systems in the metal casting industry 1
Abstract
This article offers a complete review of the research articles that are related to the application of decision support and intelligent system with specific reference to metal/die casting. Data was obtained from 89 articles that were published from 2000 to 2015 in 47 journals.
The articles are categorized based upon three different categories based on numbers of impressions, material poured and pressure application. They are further classified into 10 subsections. A widespread list of journal articles is identified in this present study that provides relevant information/references for both practitioners and researchers on the application of decision support and intelligent systems to various stages of metal/die casting.
In light of the developed classification framework, we identify gaps in extending the use of the decision support and artificial intelligent systems in the industry and suggest potential and applicable research areas for further consideration in this subject area.
Introduction
Metal casting is considered as a 7000-year-old technology which offers a large range of routes in order to produce the components with a range of sizes, shapes, quantities, quality and metal requirements (Akarte et al., 1999). Metal casting is the simplest process in which mostly gives a direct routing to the shape of the product and it gives least expensive.
The process of metal casting requires a mold cavity with the desired shape and metal that is molten is poured over the mold cavity. The main objective of the metal casting is produced beneficial implements for the human consumption and also for the beautiful work of art. From the ancient art casting, it is clear that modern industrial casting has their production which has significant skill and technological skill. In the ancient times learned and traditional skill has been used for the ages and experiences in order to produce acceptable casting.
The quality of the metal casting is affected by a number of parameters which are found at the different process stages. For example, defects that may result from improper parameters of the molding and core sand include pinholes due to the presence of hydrogen, sand deformation, gas fractures, and shape imperfections.
Defects that may result from improper construction or improper assembly of the pattern and mouldsare fractures, shape imperfections, sand presence, is runs, cracks, gas presence, surface defects, mechanical damage, knob, flash, mismatch, pushing up, warping. Gases tend to dissolve in the liquid steel at all stages of the production of castings, i.e. during melting in the furnace, during tapping, during pouring of molds, and even after pouring of the molds before complete solidification of the casting. Therefore, reducing or eliminating casting defects such as blowholes, voids in the cast structure, pinholes, non-metallic presence or porosity, and scaling on the surface of casting requires strict control of the whole process of melting and casting.
The control of charge and compliance with the technological regime during melting of alloys in a furnace for casting are particularly important in the absence of vacuum treatment of liquid metal (in an induction furnace or ladle). Possible defects caused by incorrect melting include is runs, slag presence, tears (caused by excessively high temperature), gas presence, incorrect chemical composition, and pinholes(Wilk-Kołodziejczyk et al., 2014).
The systematic review of the designer and robust in a way for evaluating the options that are available for identifying the best. The process selection is a manufacturing task in order to choose a method to transform the materials in to the one or more processes. The process considered to be more economical, and they are subjected for the meeting of technical constraints(Dieter, 1991). The manufacturing and material processing is a selection process problem in which multi-attribute decision-makingproblem.
The decision is made during the preliminary design of an environment that is uncertain in the parameters, relationship and requirements. Material and process selection (MPS) occurs before the beginning of design for manufacturing (DFM) (Karthik et al., 2003).The study indicates that the product cost is around 5% of the total product cost, and the design is made of the stage effect of the product cost (Chen and Feng, 2000).
This study, therefore, aims to provide a systematic and inclusive evaluation of research articles in order to gain insights into the applications of decision support in the metal casting system. It also aims to develop a classification framework to analyse the extant literature in this subject area to provide a reference for researchers to maximize effort value in future research.
The remaining of this paper is organised as follows. First, we propose a classification scheme for analyzing the structure categorizing the articles relating to the applications of decision support and intelligent systems in metal casting. Second, we describe the research methodology adopted in conducting the study.
Third, we scrutinize those articles in relation to our proposed framework. Fourth, we provide a discussion on the practical implications of applying such systems in the industry and identify potential areas for future research. Finally, we provide a summary and conclusion to describe the contributions as well as the limitations of the study.
Framework classifications for metal casting and decision support system
In order to understand the decision support system of metal casting we first analyse the structure industry this can be classified as follows: based upon the number of impressions, materials poured and application towards the pressure.
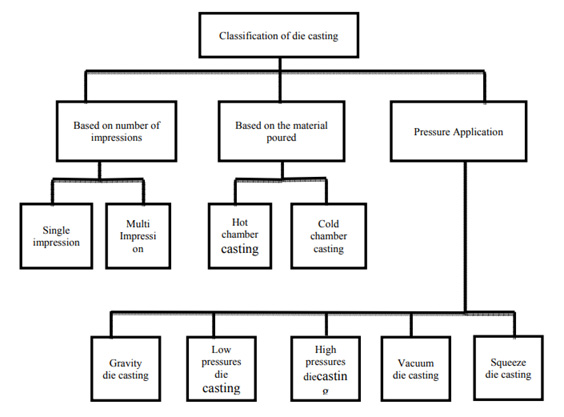
These classifications are further subdivided in to 8 types such as single impression, multi-impression, hot chamber, cold chamber; gravitydies casting, low-pressure casting, high-pressure casting, vacuum casting and squeeze casting as shown in figure 1.
Fig. 1. Classification of metal/die casting
Application of decision support and intelligent systems
There are a number of decision support and intelligent systems available in the market. In this study, we focus on the most common classifications related to decision support system.
Genetic algorithm:
Genetic algorithm (GA) is considered as an evolutionary population-based searching method. The algorithm makes use of probabilistic methods of search which is based on evolutionary and genetic principles (Chamber, 1995). GA is predominantly appropriate for solving the machine layout and scheduling problems faced metal casting (Chan et al., 1998; Hsu et al., 2009; Lin, 2009; Min and Cheng, 2006; Wong et al., 2000, 2005, 2006).
GA is used for the optimization of the hybrid metal matrix in order to get a lower rate during the dry process of sliding (Radhika et al., 2015). Particularly, GA is used in scheduling production towards the casting industry. In GA, there are two types of phases in production: moulding and melting (Landmann et al., 2007). In the metal casting, GA is used for defect study which is based on Non-destructive testing (NDT) (Kumar et al., 2015).
Artificial Neural Networks:
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) is a mathematical model based on the structure and function of biological neural networks (Liao, 2004). Rather than using traditional computer algorithms, ANN provides answers using heuristics that are similar to the human brain (Ngai et al., 2014). ANN used in metal casting is to minimize the casting defects (Singha and Singh, 2015).
The mechanical properties of the casting are yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, elongation of percentage plays a vital role in their operational life. This mechanical property can be predicted using ANN (Sata and Ravi, 2015).
Fuzzy logic:
Fuzzy logic is an approach which says the “degree of truth” that uses the mathematical theory of fuzzy sets in order to deal with perceptive estimated rather than accurate (Liao, 2004).
It is sometimes, though not exclusively; implemented using ANN. Fuzzy-logic can provide solutions to problems that involve the need to deal with approximations, uncertainty, and insufficient information (Kablan, 2014). Daws et al. (2008) aimed to propose automated advisory casting in order to develop a fuzzy model.
The fuzzy sets or models are mathematical mean which represents imprecisely and vagueness information and therefore, the term fuzzy named. In the present study, the decision model enables the preference of the designer over the decision factor which can be implemented depending upon the weighted property index (WPI) for each section.
There is a compatible rating among the product profile requirement and stored database that is an alternative to the database the fuzzy logic is generated for each decision criteria. The main objective of the fuzzy system is to solve the problems that are formed during the process evaluation and selection activates. These models have the capability of recognizing, representing, manipulating, interpreting, and utilizing data and information that are vague and lack certainty. A ranked set of compatible alternative processes is output by the system.
The study concludes that this approach is benefited by the existing system that is armed with the decision module or a database since it can be applied to all type of shape, casting or material. However, the limitation is the compatibility that is obtained from this system that may vary from parts to part from manufacturer.
Knowledge based system (KBS):
Knowledge-based systems (KBS) are rule-based systems (Mahapatra, 1997) that incorporate database with a knowledge expert with linkages and coupling design in order to contribute the information retrieval system in response to specific queries and to make quick and effective decisions (Laudon and Laudon, 2002; Wiig, 1994).
In the metal casting, the manufacturing knowledge is combined with the handbooks, design which is converted in to formal rule in terms of the system expert. In this, the rules are extracted manually through the guidelines and design parameters which can be split by the design stored and rules. Separating the rules are formed from the stored generic value which is possible to increase the repetition and avoids the flexibility to the knowledge base.
It is found that when a rule is passed, the generator advice uses relevant facts that are quantified material and manufacturing process (Lockett and Guenov, 2007). This system can be of potential benefit to casting product designers, as well as foundry engineers, in identifying the most suitable casting process for a given specific design and for assessing a given design for a preferred casting process (Er et al., 1996).
Decision support system (DSS):
Decision support system (DSS) is considered as a computer based system which can be involved in helping the decision makers in order to use models and data and to solve identified problems. (Rauscher, 1999); practically to automate a variety of tasks and to facilitate optimal decision-making within a given supply chain.
DSS is designed in such a way that they provide sources towards the expertise which are unavailable and acts as a uniform source of knowledge which can be updated in order to merge the emerging new technologies (Plant and Hu, 1992). Because in many situations the quality of decisions is important, aiding the deficiencies of human judgment and decision making has been a major focus of science throughout history.
Disciplines such as statistics, economics, and operations research developed various methods for making rational choices. More recently, these methods, often enhanced by a variety of techniques originating from information science, cognitive psychology, and artificial intelligence, have been implemented in the form of computer programs, either as stand-alone tools or as integrated computing environments for complex decision making.
Such environments are often given the common name of decision support systems (DSSs). The concept of DSS is extremely broad, and its definitions vary, depending on the author’s point of view. To avoid exclusion of any of the existing types of DSSs, we will define them roughly as interactive computer-based systems that aid users in judgment and choice activities.
Another name sometimes used as a synonym for DSS is knowledge-based systems, which refers to their attempt to formalize domain knowledge so that it is amenable to mechanized reasoning. Decision support systems are gaining an increased popularity in various domains, including business, engineering, the military, and medicine.
They are especially valuable in situations in which the amount of available information is prohibitive for the intuition of an unaided human decision maker and in which precision and optimality are of importance. Decision support systems can aid human cognitive deficiencies by integrating various sources of information, providing intelligent access to relevant knowledge, and aiding the process of structuring decisions.
Research methodology
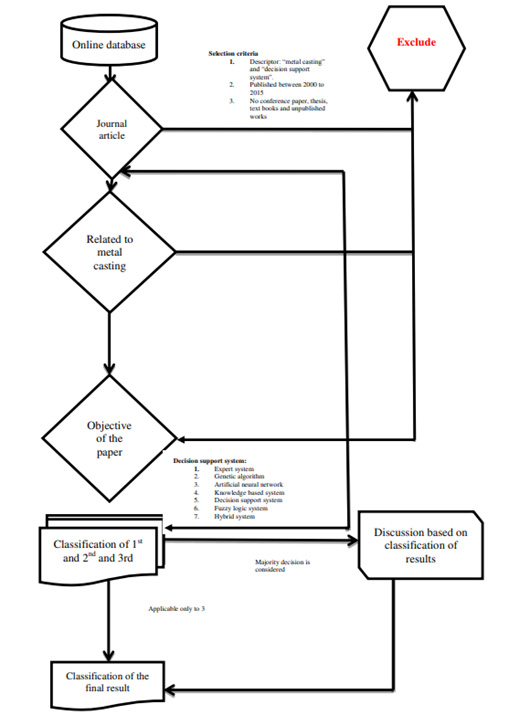
In order to identify the extant literature review that is relevant to the present study, the study has adopted a framework developed by Ngai, Xiu and Chau (2009) for the selection of material as shown in figure 1. There are 4 phases in the framework (1) online database search, (2) first researcher classification, (3) individual verification of the results that are classified by the second researcher, and (4) Third researcher verification of the results.
First, the study has selected five dominant online databases (Elsevier, IEEE, Science direct, Springer, and Emerald) and formed the external and confined the review to the extant literature exclusively found in journal articles referenced by these databases.
This is because peer-reviewed journals are the most common forum in which researchers publish the findings of their work. We excluded conference papers, theses, dissertations, newspapers, textbooks, and unpublished papers; if these have relevant and efficacious content, they are likely to be a precursor to a subsequent journal publication.
With the use of the direct keywords search, we are selecting the articles that are related to decision and intelligent support system in metal casting; the articles are filtered using the keywords ‘casting,’ ‘predesign casting,’ ‘metals’ and ‘material selection.’
The searches included in the system are GA, ANN, fuzzy logic, KBS, and DSS. Overall around 47 journals articles were selected from 30 journals. The sample size considered is about 15 years from the 2000 to 2015. Hence, the review is focused towards the academic search activity, and it is found that the selected research is relevant to the present industry priorities and features.
In order to develop a classification framework, the articles were reviewed and analyzed in a detailed manner in order to reduce the bias to the researchers.
Each reviewer provides his/ her own views in 1) the metal casting process; 2) Decision support and the intelligent systems that are adopted in each paper; 3) the objective of the paper; 4) the main contribution in understanding the metal casting process. In addition, the articles are classified according to the journal and publication. Selection criteria for the framework and evaluation process as discussed above are briefly shown in figure 2below with help of a flowchart.
Fig. 2. Selection criteria for the framework and evaluation process